4. Topic API Overview¶
The RnR Service can be controlled and monitored using a DDS topic API.
All topics are in a separate DDS partition called RecordAndReplay.
4.1. Record & Replay topics¶
Name |
Type |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Controlling the Record and Replay service |
|
|
Controlling the Record and Replay service (version 2) |
|
|
Monitoring status of scenarios |
|
|
Monitoring status of services |
|
|
Monitoring status of storages |
|
|
Monitoring data-characteristics of storages |
4.2. Relevant QoS settings¶
The following table shows the topic QoS parameters that deviate from the default DDS topic QoS, for the topics used by the Record and Replay Service.
Policy |
Scenario Topic |
Status + Statistics Topics |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This enables readers and writers to use the copy_from_topic_qos() operations
or the USE_TOPIC_QOS convenience macro to create a reader or writer that is
compatible with the topics created by the service. Furthermore the status topic
writers use a KEEP_ALL history QoS so readers can get a full overview of all status
updates instead of only the last state. The scenario readers are created with a
VOLATILE durability so they are also able to read samples produced by a VOLATILE
writer in addition to TRANSIENT and PERSISTENT writers.
The corresponding IDL code can be found in the RnR Topic API specification.
4.3. Command Type¶
Command Topic
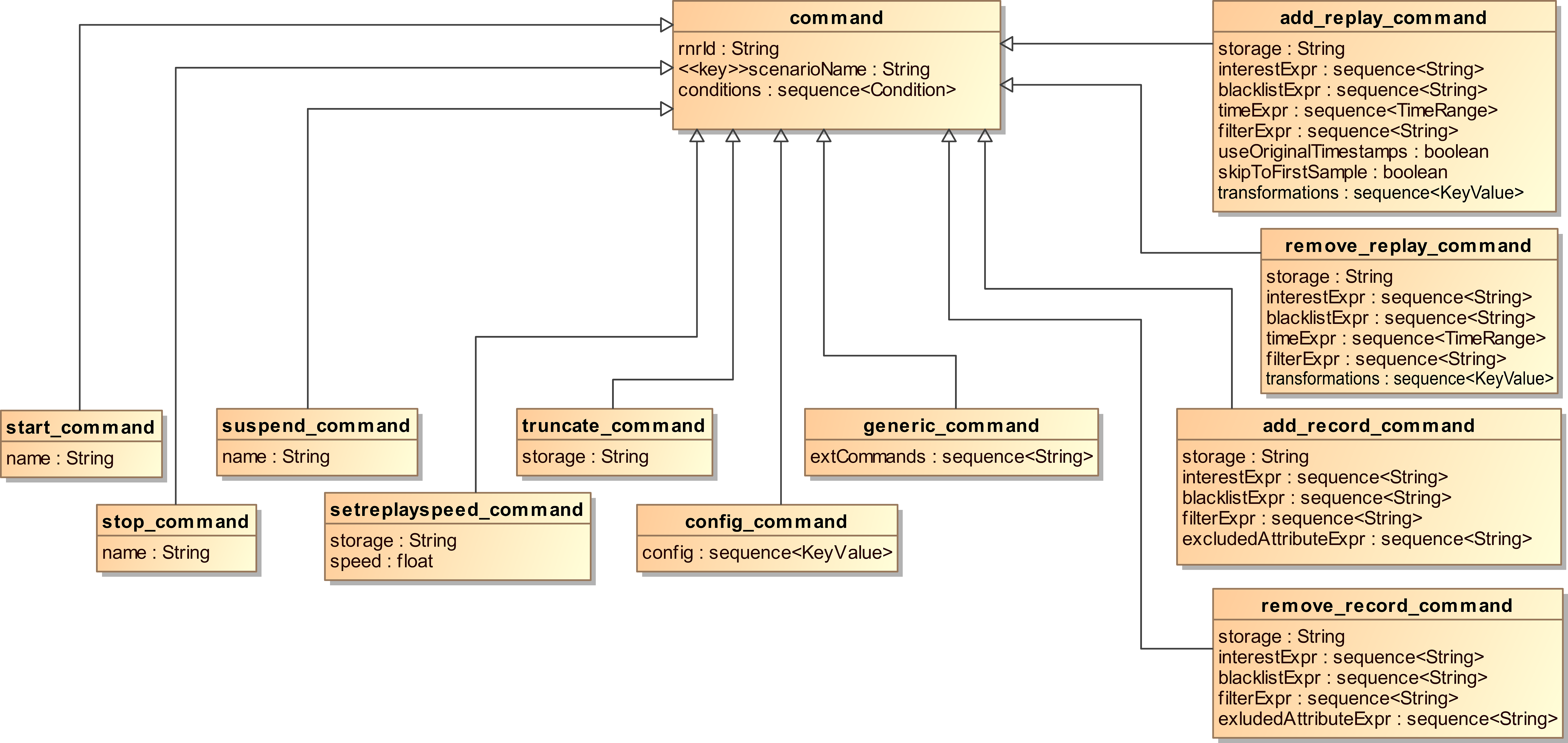
The command type, used by the rr_scenario and rr_scenario_v2 topics,
contains a union that allows the command kind to be set. Depending on the
command kind, certain members are available that apply only to a specific
type of command.
The following command kinds can be set when creating a command:
- START_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Start a scenario (or continue a paused scenario).
- STOP_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Stop a running scenario.
- SUSPEND_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Suspend processing of new commands in a running scenario.
- CONFIG_COMMAND
Modify the runtime configuration of a RnR service.
- SETREPLAYSPEED_COMMAND
Change the replay-speed of a storage.
- TRUNCATE_COMMAND
Remove data from a storage.
- ADD_RECORD_COMMAND
Specify interest to record data to a storage.
- REMOVE_RECORD_COMMAND
Remove record-interest from a storage.
- ADD_REPLAY_COMMAND
Specify interest to replay data from a storage.
- REMOVE_REPLAY_COMMAND
Remove replay-interest from a storage.
There are a number of common properties that are shared by all commands:
- rnrId
The
rnrIdis used to address the command to a specific RnR service. It should match the name attribute of the service tag in the OpenSplice configuration. The middleware uses this identifier to resolve the configuration options that apply to the service. A RnR service only accepts commands with an rnrId that matches its service-name. An asterisk*can be used as rnrId for commands targeted at all available RnR services in a domain.- scenarioName
The
scenarioNameis the key of the scenario topic. It is used to uniquely identify a specific scenario instance of which all samples (commands) together make up the scenario. For more information about scenarios, please see the section on Scenarios.- conditions
Optionally one or more conditions can be attached to a command. The command is only processed when all conditions are met.
 Currently only one kind of condition is supported: the
time-stamp condition. Future extensions will add other kinds
of conditions which is the reason why the API supports attaching
multiple conditions to a command.
Currently only one kind of condition is supported: the
time-stamp condition. Future extensions will add other kinds
of conditions which is the reason why the API supports attaching
multiple conditions to a command.
4.3.1. Control commands¶
Some kinds of commands are used to control the running state of a scenario: the start, stop and suspend commands.
These all have a single member.
- name
The name of the target scenario to control.
 Do not confuse this with
Do not confuse this with scenarioName, which is the name of the scenario that will process the command.- START_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Instructs the service to start processing scenario name. The service will publish a status update that changes the state of the scenario to
RUNNING. If the target scenario is already known to the service, and is in the suspended state, a start command causes the scenario to resume processing commands, changing the scenario status fromPAUSEDtoRUNNING.- SUSPEND_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Suspends the processing of commands by the scenario. This allows applications to submit a number of commands to a scenario, without any immediate effects. When the scenario is resumed all new commands are processed as if they were published in a batch while in reality they may have been published with varying intervals.
- STOP_SCENARIO_COMMAND
Stops the execution of a scenario, including any recording and/or replaying that was defined as part of that scenario.

It is important to understand that a scenario, once stopped, cannot be started again. However, it is possible to start a new scenario with the same name as the stopped scenario. If any commands of the original scenario were published as transient data they will be delivered to and processed by the new scenario, giving the impression that the scenario has been re-started.
4.3.2. Config command¶
Config commands are used to modify the runtime configuration of a RnR service.
- config
A sequence of
KeyValueobjects.
A config command can be used to add a storage to the service or modify
properties of an existing storage. Storages can also be configured in the OpenSplice
configuration file, but config commands provide the opportunity to create and
configure storages dynamically.
A single config command can apply to multiple storages, if the config
sequence consists of multiple elements. The key of the KeyValue object
should always be Storage.

Currently, only storages can be manipulated by
configcommands but future versions may enableconfigcommands to modify other aspects of the service, using different keys.
The value for Storage configuration data is a string describing the storage in XML notation. The format of this XML string is identical to the XML used in the configuration file (created by the OpenSplice configuration tool).
An example:
command {
scenarioName = “MyScenario”,
rnrId = “MyService”,
conditions = NULL,
kind = CONFIG_COMMAND,
config[0].keyval = “Storage”,
config[0].sValue = “<Storage name='MyStorage'>
<rr_storageAttrXML>
<filename>my-storage.dat</filename>
</rr_storageAttrXML>
<Statistics enabled=”true” publish_interval=”30”/>
</Storage>”
};
When a config command is issued for an existing storage, the storage
properties are modified accordingly.

Note that storage attributes can only be changed when a storage is unused: it cannot be in the
OPENstate (see Storage Status). Properties related to statistics can be modified while the storage is in use.
4.3.3. ADD_RECORD_COMMAND¶
This command is used to add interest to record certain DDS data.
Mandatory properties:
- storage
The name of the storage in which the data has to be stored. If the storage cannot be resolved the command is ignored.
Available storages can be determined by subscribing to the
StorageStatustopic.- interestExpr
A sequence of strings that describe the record interest. Each expression is a partition-topic combination where the partition- and topic-expression are separated by a period (
‘.’). Wildcards are supported:‘?’to match a single character and‘*’to match any number of characters. If expressions overlap, even if only partially, data will only be recorded once.
4.3.4. REMOVE_RECORD_COMMAND¶
This command mirrors the add record command and is used to remove record interest from a storage.
Mandatory properties:
4.3.5. ADD_REPLAY_COMMAND¶
This command is similar to a record command but adds interest to replay data to the Record and Replay service.
Mandatory properties:
- storage
The name of the storage from which the data will be replayed. If the storage cannot be resolved the command is ignored.
Available storages can be determined by subscribing to the
StorageStatustopic.- interestExpr
A sequence of strings that describe the replay interest. Each expression is a partition-topic combination where the partition- and topic-expression are separated by a period (
‘.’). Wildcards are supported:‘?’to match a single character and‘*’to match any number of characters. If expressions overlap, even if only partially, data will only be recorded once.
Optional properties:
- timeExpr
A sequence of time-ranges that are used in combination with the interest expressions to select a subset of data available in a storage for replay. Each time-range in the sequence is applied to each interest expression. A sample read from a storage is only replayed if its partition and topic can be matched against the interest expressions and its record-time can be matched against the time-range expressions. The time-range expressions are optional; when they are omitted a sample is replayed when an interest expression matches. For more information about time-ranges, see the description of the TimeRange type.
- useOriginalTimestamps
By default this value is
true. When a sample is recorded, its original write and allocation timestamps are preserved. When this sample is replayed, it will be delivered to readers with these original timestamps. Depending on resource limits and QoS settings, readers may discard the replayed data if data with more recent timestamps is available. By settinguseOriginalTimestampstofalse, the timestamps will be updated with the current time upon replay.- skipToFirstSample
By default this value is
false. When a sample matches interest expressions but doesn’t match any of the supplied time-ranges, the Record and Replay service tries to mimic original timing behaviour by sleeping until the next sample is evaluated based on record timestamps. Sometimes this is not the required behavior and the service should simply skip all non-matching samples and start replaying immediately the first sample that matches an interest expression and time-range. This behaviour can be enabled by settingskipToFirstSampletotrue.
The following property is only available in version 2 of the RnR scenario topic.
- transformations
A sequence of transformations, applied to each sample upon replay. By default, no transformations are applied. Note that samples first have to match interest-expression and time-range before any transformations are evaluated. The transformations sequence consists of
KeyValueelements. A specific type of transformation is selected by choosing a specific key. Multiple transformations of the same kind can be used in the same sequence. The value is a string describing the new value. The transformation can be applied conditionally by using a‘:’(colon) character to separate original and replacement values in the value-string. Note that the original value needs to be an exact match, wildcards or expressions are not supported. The supported transformations types are listed in the table.Key
Description
partitionPartition in which the sample is replayed
deadline_periodDeadline QoS policy
latency_periodLatency budget QoS policy
ownership_strengthOwnership strength QoS policy (applies only to samples written with exclusive ownership-kind QoS policy)
transport_priorityTransport priority QoS policy
lifespan_periodLifespan QoS policy
Transformations that involve a period can be expressed in either DDS-compliant duration (sec.nanosec) or more human-friendly floating-point (sec.millis) formats. Floating-point values are interpreted locale-independent, using a period
‘.’(decimal point) character. Partition transformations are supported for partition names consisting of alphanumeric and special characters‘-’,‘/’and‘_’.
4.3.6. REMOVE_REPLAY_COMMAND¶
This command mirrors the ADD_REPLAY_COMMAND, except for the properties
useOriginalTimestamps and skipToFirstSample, which change the replay
behaviour and are not applicable to the remove replay command.
The command is used to remove replay interest from a storage. Mandatory members of the add replay command are also mandatory in the remove replay command.
Mandatory properties:
- storage
The name of the storage which replay-interest is removed from.
- interestExpr
The interest expressions describing the replay interest to remove.
 Note that these interest expressions need to match those used
previously in an add replay command.
Note that these interest expressions need to match those used
previously in an add replay command.
Optional properties:
- timeExpr
The sequence of time ranges to remove. Similar to the add replay command. If this parameter is specified, only the interest that exactly matches the time ranges is removed. As a shortcut, if the time range sequence is empty, any interest that matches the interest expressions in the remove replay command is removed regardless of the time ranges attached to that interest.

The following property is only available in version 2 of the RnR scenario topic.
- transformations
A sequence of transformations to remove. If any replay interest is to be removed completely, this sequence should match exactly the sequence included in add replay command(s) responsible for adding the interest. For more details about the contents of the
KeyValuesequence elements, please see the ADD_REPLAY_COMMAND.
4.3.7. TRUNCATE_COMMAND¶
This command can be used to clear a storage. When recording samples to an existing storage, by defauilt the data is appended. If instead the required behaviour is to overwrite the storage, the truncate command can be used to remove the data recorded to the storage during previous sessions.

Note that the truncate command can only be executed if the storage isn’t busy recording and/or replaying data. Thus is may be required to first publish remove record/replay commands, in order to remove all interest from a storage so that it gets closed by the RnR service, before the truncate command can be succesfully processed. The
StorageStatustopic should be monitored to determine if this is the case.
4.3.8. SETREPLAYSPEED_COMMAND¶
Using this command the replay speed of a storage can be manipulated. The replay
speed affects the delay between replayed samples. For example, a replay speed
of 2 will cut the delay in half: samples will be replayed twice as fast
as originally recorded.
Mandatory properties:
- storage
The name of the storage of which to change the replay speed. If the storage cannot be resolved the command is ignored.
- speed
A floating-point value containing the new replay-speed. The following values have a special meaning:
-1: Maximum speed; delays between samples are skipped and the samples from the storage are inserted into DDS as fast as possible.1: Replay samples with the same timing characteristics as when originally recorded.0: Pause the storage; no samples are replayed until the speed is increased.The default replay speed is
1(samples are replayed with the same timing characteristics as when originally recorded).
4.4. Status Types¶
To monitor the status of various components of the service, applications can take a subscription on the status topics published by the Record and Replay service.
Status Topics
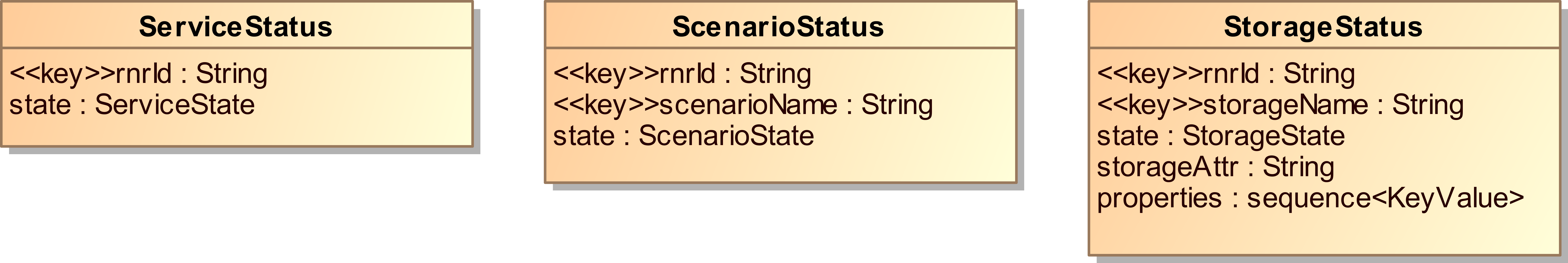
Status topics are state-based, meaning that they are only published when a state
changes. Readers normally only need to read the latest sample of an instance to get
the latest (current) state. However, a reader can also be created with a KEEP_ALL
history if it needs to be aware of all states even when state changes occur in quick
succession.
4.4.1. Service Status¶
Each Record and Replay service publishes its own state in the rr_serviceStatus
topic. The topic uses the ServiceStatus type, which has the following members:
- rnrId
The name identifying the service. This is also the key of the topic. The
rnrIdcan be used to identify the service responsible for publishing the status update.- state
The current state of the service. The following states are possible:
INITIALISING: The service is started and initialising, but not yet able to process commands. During initialization the service processes configuration parameters and joins the DDS domain.OPERATIONAL: The service is successfully initialized and ready to accept commands.TERMINATING: The service is shutting down.TERMINATED: The service is detached from the DDS domain and stopped.
The service status topic reflects the life-cycle of a Record and
Replay service. It is published when the state field changes,
which normally occurs only during service startup or shutdown
(i.e. when OpenSplice is started or stopped).
4.4.2. Scenario Status¶
The service publishes the state of each known scenario in the
rr_scenarioStatus topic. This topic, using the ScenarioStatus
type, contains the following members:
- rnrId
The name identifying the service.
- scenarioName
The name identifying a scenario.
The scenarioName combined with the rnrId define an instance of
the scenario status topic, so each update can be related to the service
and scenario responsible for that status.
- state
The current state of the scenario. The following states are possible:
RUNNING: The scenario is running and actively processing commands.SUSPENDED: A scenario enters the suspended state after a suspend-scenario command is processed for the scenario. While suspended, the scenario doesn’t process any new commands.STOPPED: The scenario was stopped and removed from the service.
Note that, until a scenario is started, a service is unaware of its existence. There may be commands belonging to the scenario, maintained by OpenSplice (in persistent or transient stores), but a scenario status isn’t published until the state of a scenario within a service is changed to
RUNNINGby issuing a start-scenario command for that scenario to a specific service.
4.4.3. Storage Status¶
The service publishes the state of each known storage in the
rr_storageStatus topic. This topic, using the StorageStatus
type, contains the following members:
- rnrId
The name identifying the service. This is a key of the topic.
- storageName
The name identifying a storage.
The storageName combined with the rnrId define an instance
of the storage status topic and can be used to relate an update
of the topic to the service and storage responsible.
- state
The current state of the storage. A storage may have the following states:
READY: This is the initial state after configuring a storage, when the configuration is deemed valid. It means the storage was defined and available when configured. In the case of a pre-existing storage, properties are available in the status update for this state.OPEN: The storage is in use by one or more scenarios identified by thescenarioNamessequence in the status update for this state.ERROR: The storage is invalid and cannot be used. This can either mean an error in the storage configuration or an issue related to resources claimed by the storage. Most notably in case of an XMLstorage, the service may not have permission to open a file that is part of the storage. Note that it is not currently possible to determine the reason for
an
Note that it is not currently possible to determine the reason for
an ERRORstate directly from the status update, but a descriptive message is written to the OpenSplice log files. A future release will make this message available in the status update.OUTOFRESOURCES: When a storage is used for recording, it may run out of resources.CLOSED: A storage may enter the closed state for two reasons. Usually it is closed when all record and/or replay interest has been detached from the storage. This occurs when all scenarios that were using the storage are stopped. If the storage is used for replay, it may also be closed when all data in the storage has been evaluated and the end of the storage was reached.- storageAttr
The XML string describing the attributes currently used by the storage. This is identical to the attributes section of a storage configuration.
- properties
Properties of the data contained in a storage. The following properties are available per recorded topic:
Partition and topic names
Number of samples and number of bytes
Record timestamps of the first and last occurrence
Average data rate
![]() Note that properties are not updated while a storage is open, they are
only updated when the state of a storage changes.
Note that properties are not updated while a storage is open, they are
only updated when the state of a storage changes.
Unlike the other status topics, the storage status is determined by more
than just the state field. The attributes and sequence of scenario
names are also part of the state. Therefore storage status updates not
only occur when the state field itself is changed but also when the
attributes are changed or when a scenario starts (or stops)
using the storage.
4.5. Storage Statistics¶
The Record and Replay service can optionally maintain runtime statistics
regarding the data that is recorded to and/or replayed from a storage.
These statistics can be published in the rr_storageStatistics topic.
Storage Statistics Topic
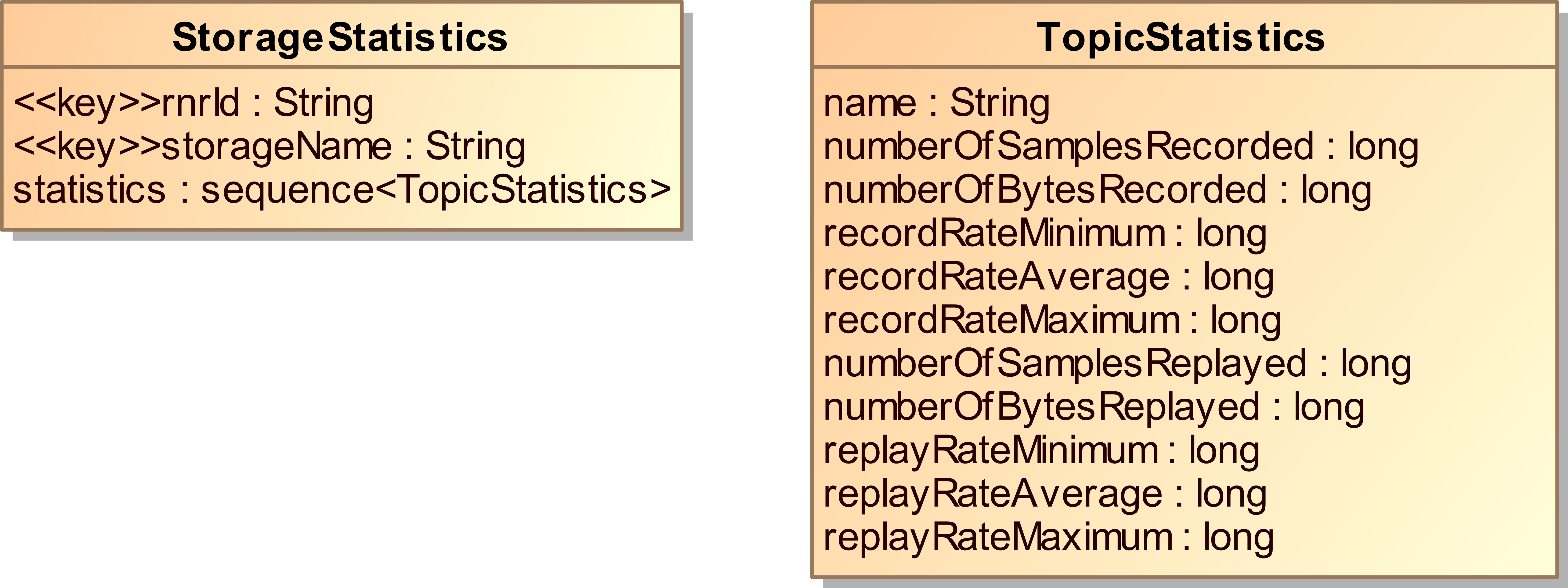
Statistics are enabled per storage. Publication in the
rr_storageStatistics topic is optional and can be managed
by the publish_interval attribute of the statistics
configuration element.
- Publish_interval
This is the number of seconds between each publication of the statistics from a specific storage. The value
-1has a special meaning: if set, the statistics will only be published when the storage is closed. Setting thepublish_intervalto0will also prevent the publication of statistics. Note that a config command can be issued to change the publication interval on the fly.
The statistics values can be reset by setting the reset attribute
in the XML configuration string of the storage statistics.
4.6. Miscellaneous Types¶
The API contains a number of utility types used as members in one or more topics. These helper types are described in this section.
Miscellaneous Types
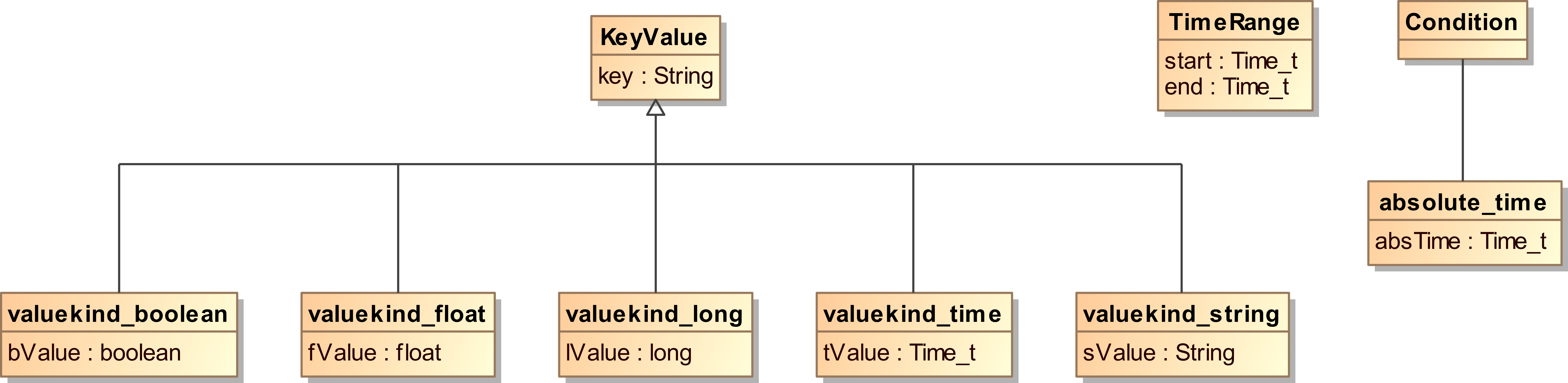
4.6.1. KeyValue¶
The KeyValue type is a generic key:value container.
It is used for the transformations sequence in add and remove
replay commands and as the config sequence of a config command,
to send configuration values to a Record and Replay service
and/or scenario.
- key
A string that selects a specific configuration value to add or update.
Depending on the KeyValue kind, a value can take on a number
of representations: boolean, string, long or float.
4.6.2. TimeRange¶
The TimeRange type can be used to limit the selection of data
in a replay command. Interest expressions select data based on
partition and topic names, time-ranges filter this selection based
on record timestamps.
The DDS::Time_t type is used to express a timestamp. A range
is defined by a start and an end timestamp.
- start
The start timestamp of the range. When
TIME_INVALID_SECandTIME_INVALID_NSECare specified, the start time is considered to be-infinity. This means that any sample recorded before theendtimestamp is matched.- end
The end timestamp of the range. When
TIME_INVALID_SECandTIME_INVALID_NSECare specified, the end time is considered to be+infinity. This means that any sample recorded after thestarttimestamp is matched.
