3. How to deploy and configure Vortex Link?¶
The first thing to define when deploying and configuring Vortex Link is the kind of deployment that should be used to satisfy the needs of the system you want to set up.
3.1. Device-to-Device & Device-to-Link¶
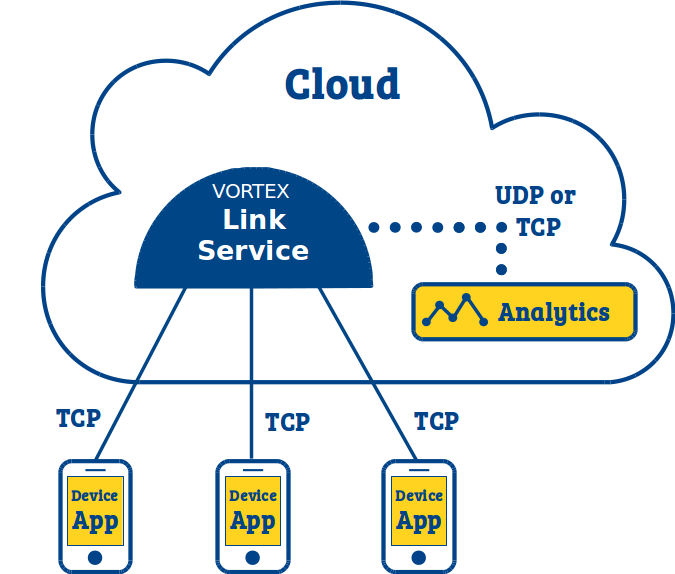
If you simply need to make several applications using TCP transport and spread over internet (devices) to communicate with each other using DDS then you typically need a Device-to-Device deployment.
If you also need some applications deployed in the cloud (typically analytics) and using TCP or UDP transport to participate to the DDS domain with the device applications then you typically need a Device-to-Device & Device-to-Cloud deployment.
For such deployment you simply need to deploy a single Vortex Link service in a cloud or any host that has a public IP address or is publicly accessible.
Configure the Vortex Link service
There is nothing mandatory to configure here. You can simply run a Vortex Link service somewhere in the cloud.
java -jar link-service.jar
You may anyway want to configure :
- The tcp port the service will listen on for incomming TCP connections : link.tcp.port (default 7400).
- The domainid that should be used to discover local applications running in the cloud and using UDP multicast : link.domainid (default 0).
- The public address of the host running the service. If the host running the service has a private address but is reachable from the rest of the world through a public address, then you need to specify this public address using the link.externalNetworkAddresses property.
Configure the device applications
When running end-user applications, we need to configure them to use the TCP transport and to point them to the Vortex Link service. Here is an example of such a configuration starting a Vortex Café application:
java -Dddsi.network.udp.enabled=false -Dddsi.discovery.tcp.peers=ip_service:7400 -jar ishapes.jar
Configure the cloud applications (analytics)
If the cloud supports multicast communications, then you have nothing particular to configure here. You only need to make sure that the domain id used by the application is the same than the one configured in the Vortex Link service (link.domainid).
If the cloud does not support multicast communications, then you need to configure cloud applications to use the TCP transport and to point them to the Vortex Link service, as done for any device application.
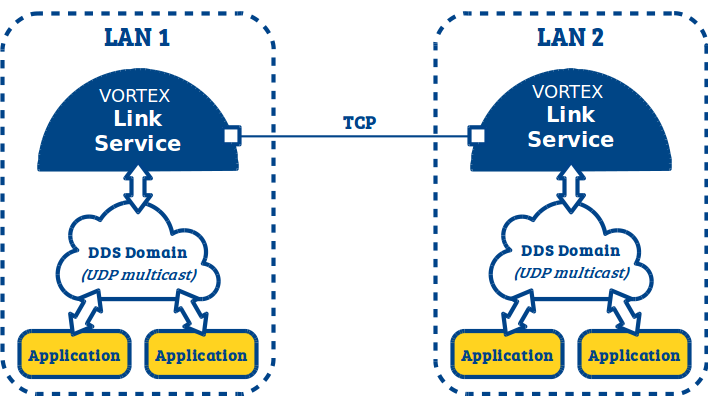
3.2. LAN to LAN¶
If you want to interconnect two or more sub systems (potentially legacy systems) each one running a DDS domain in a LAN using UDP multicast then you typically need a LAN-to-LAN deployment.
For such deployment, you need to deploy a single Vortex Link service in each sub system (LAN) on a host that is publically accessible.
You will have to make sure that :
- Each deployed Vortex Link service is configured with the proper domainid to discover local applications through UDP multicast
- Each deployed Vortex Link service is configured to connect to the other services.
If the vortex Link services are deployed on hosts that cannot directly connect to each other (behind a symetric NAT) then you need an Indirect LAN to LAN deployment.
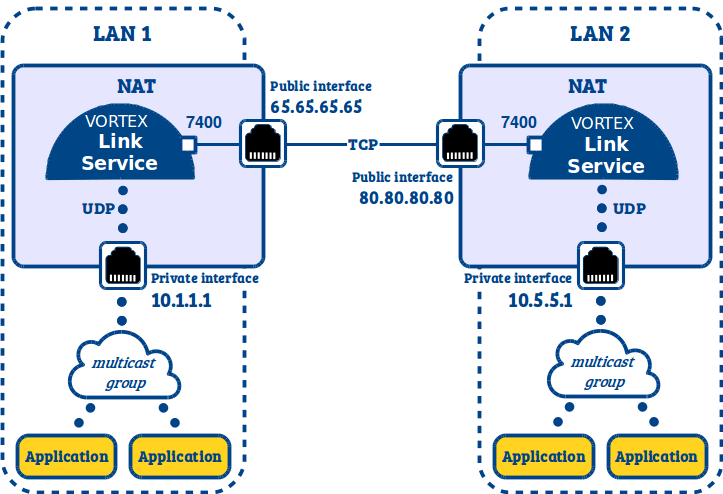
3.2.1. Vortex Link services deployed on the NAT hosts¶
Each sub system is generally deployed behind a NAT host. A NAT host typically has two network interfaces : one interface with a private IP address that communicates with the sub system hosts and one interface with a public address accessible from the rest of the world.
If you can deploy your Vortex Link services in those NAT hosts, you will have to :
- Configure the Vortex Link services to use the public interface for TCP communications.
- Configure the Vortex Link services to use the private interface for UDP communications.
- Configure the Vortex Link services to connect to each other using their public addresses.
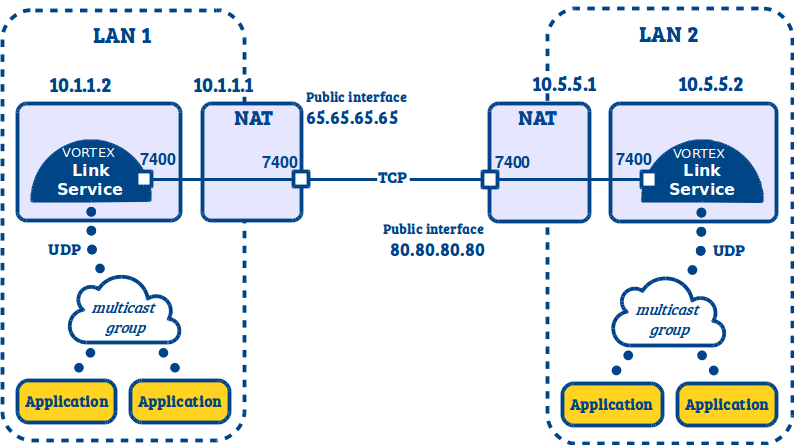
Vortex Link service configuration for LAN 1
java
-Dlink.domainid=0
-Dlink.tcp.interface=65.65.65.65
-Dlink.udp.interface=10.1.1.1
-Dlink.tcp.peers=80.80.80.80:7400
-jar link-service.jar
Vortex Link service configuration for LAN 2
java
-Dlink.domainid=0
-Dlink.tcp.interface=80.80.80.80
-Dlink.udp.interface=10.5.5.1
-Dlink.tcp.peers=65.65.65.65:7400
-jar link-service.jar
3.2.2. NAT hosts configured for ports redirection¶
If you can’t deploy your Vortex Link services in the NAT hosts, maybe you can configure your NAT to redirect ports to a given host in the sub system (LAN), so that this host is accessible from the outside world (using the NAT public address).
If so, you can deploy your Vortex Link services on those publicly accessible hosts and make sure that they can connect to each other. You will have to :
- Configure the Vortex Link services with the public IP address of the NAT host of their sub system with the help of the link.externalNetworkAddresses option.
- Configure the Vortex Link services to connect to each other using the public IP addresses of their respective NAT hosts.
Vortex Link service configuration for LAN 1
java -Dlink.domainid=0 -Dlink.tcp.peers=80.80.80.80:7400 -Dlink.externalNetworkAddresses=65.65.65.65 -jar link-service.jar
Vortex Link service configuration for LAN 2
java -Dlink.domainid=0 -Dlink.tcp.peers=65.65.65.65:7400 -Dlink.externalNetworkAddresses=80.80.80.80 -jar link-service.jar
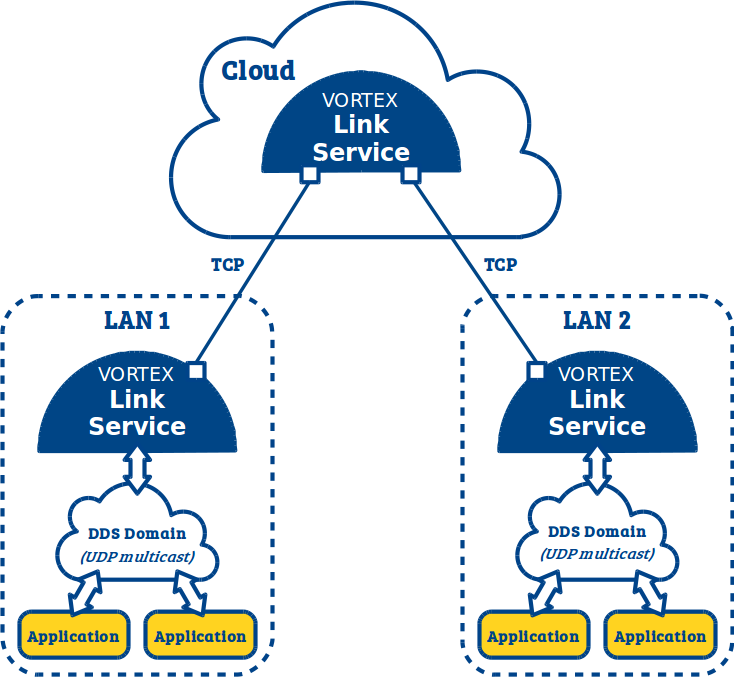
3.3. Indirect LAN to LAN¶
If you want to interconnect two or more sub systems (LAN-to-LAN deployment) but need to deploy your Vortex Link services on hosts that have no public address and are not publicly accessible, then you need to deploy a single Vortex Link service in each sub system (LAN) but you also need to deploy a Vortex Link service on a public host, typically in a cloud. This extra Vortex Link service will act as an intermediary between the sub systems and route data between them.
You will have to make sure that :
- Each Vortex Link service deployed in a sub system is configured with the domainid used by the UDP applications deployed in the sub system (LAN).
- Each Vortex Link service deployed in a sub system is configured to connect to the Vortex Link service deployed in the cloud.
- The Vortex Link service deployed in the cloud is configured with a service level (link.serviceLevel) greater than the service level configured on the Vortex Link services deployed in the sub systems (default 0).
Configure the Vortex Link service running in the cloud
java -Dlink.serviceLevel=1 -jar link-service.jar
Configure the Vortex Link services running in the sub systems
java -Dlink.domainid=0 -Dlink.tcp.peers=link_host_ip:7400 -jar link-service.jar
Configure the sub systems applications
There is nothing particular to configure for the sub systems applications. By default they will use UDP multicast and be discovered and routed by the Vortex Link services.